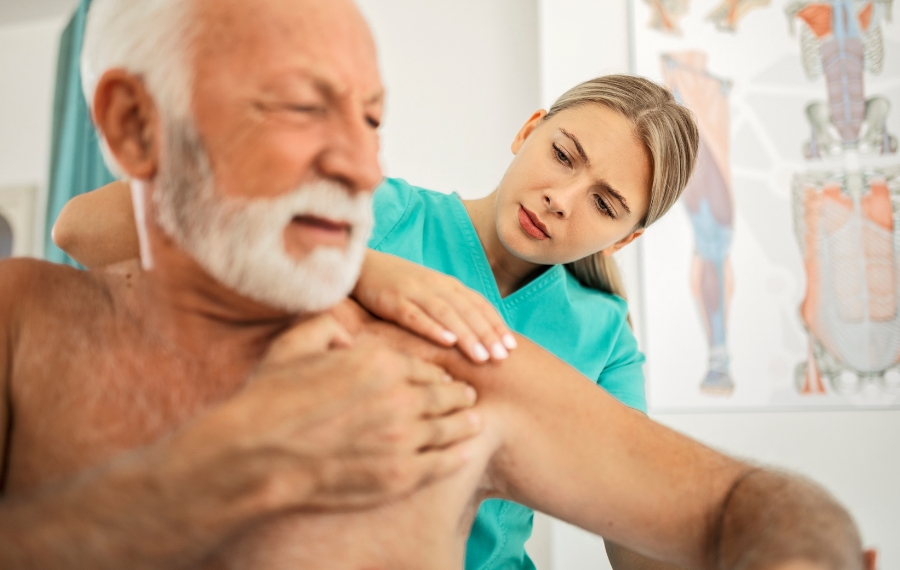
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, providing stability and facilitating a wide range of motion. Rotator cuff injuries are common, often caused by overuse, trauma, or degenerative changes. These injuries can lead to pain, weakness, and restricted shoulder function. Physiotherapy plays a critical role in the treatment and rehabilitation of rotator cuff injuries. This article provides an overview of rotator cuff injuries, discusses common treatment methods, and highlights the importance of physiotherapy in the recovery process.
Understanding Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff is susceptible to several types of injuries, including:
- Rotator Cuff Tendinitis: involves inflammation or irritation of the rotator cuff tendons, often caused by repetitive overhead activities or poor shoulder mechanics.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: These tears can be either partial or full-thickness tears, and they can occur as a result of acute trauma or degenerative changes over time. Rotator cuff tears may cause significant pain, weakness, and limited shoulder mobility.
Physiotherapy Treatment Methods for Rotator Cuff Injuries
- Pain and Inflammation Management: Physiotherapists employ various modalities, such as cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation, to reduce pain and inflammation in the affected area1. These techniques can help alleviate symptoms and facilitate the healing process.
- Range of Motion Exercises: Physiotherapists prescribe specific exercises to improve shoulder range of motion, addressing stiffness and restoring normal joint mobility. These exercises may include pendulum swings, passive and active-assisted range of motion exercises, and gentle stretching techniques.2
- Strengthening Exercises: Once pain and inflammation are under control, physiotherapists develop individualized strengthening programs to target the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles. These exercises aim to restore strength and stability to the shoulder joint. Initially, resistance bands, isometric exercises, and light weights may be used, gradually progressing to more challenging exercises.3
- Manual Therapy: Physiotherapists may utilize manual therapy techniques, including joint mobilizations, soft tissue massage, and myofascial release, to alleviate muscle tightness, improve tissue extensibility, and promote healing.4
- Biomechanical Assessment and Correction: Physiotherapists assess the individual’s movement patterns and biomechanics to identify any contributing factors or abnormalities that may have led to the injury. They then implement corrective measures, such as posture correction, ergonomic modifications, and movement retraining, to reduce stress on the rotator cuff and promote optimal shoulder mechanics.5
- Functional Rehabilitation: Physiotherapists focus on functional exercises that mimic everyday activities or specific sports movements to improve overall shoulder function and facilitate a safe return to normal activities.6
- Patient Education and Self-Management: Physiotherapists provide education on proper body mechanics, ergonomics, and strategies to prevent further injury. They also guide individuals on self-management techniques, including home exercises, activity modifications, and pain management strategies.7
Conclusion
Rotator cuff injuries can significantly impact shoulder function and quality of life. Physiotherapy plays a vital role in the treatment and rehabilitation of these injuries. Through a combination of pain management, range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, manual therapy, biomechanical assessment, functional rehabilitation, and patient education, physiotherapists help individuals recover from rotator cuff injuries and regain optimal shoulder function.
The Physiotherapy Centre Physio team are here to help. Give us a call on 01795 435060 to make an appointment for progressive treatment and rehabilitation advice.
Bibliography:
- Atik A, Esenyel CZ, Erkmen N, Öztürk H. The effect of kinesio taping on muscle pain, functional status and sleep quality in patients with rotator cuff tendinopathy: A randomized controlled study. Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. 2017;30(5):1059-1066. doi:10.3233/BMR-150626
- Houghton K, Clark P, Lockhart-Wheeler K. Exercise interventions for the treatment of chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clinical Rehabilitation. 2019;33(10):1630-1643. doi:10.1177/0269215519843053
- Kuhn JE. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement: A systematic review and a synthesized evidence-based rehabilitation protocol. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2009;18(1):138-160. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.06.004
- Page P, Frank C, Lardner R. Assessment and Treatment of Muscle Imbalance: The Janda Approach. Human Kinetics; 2010.
- Roy JS, MacDermid JC, Woodhouse LJ. A systematic review of the psychometric properties of the Constant-Murley score. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2010;19(1):157-164. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2009.04.013
- S?dal E, Dilek B, Öztürk Y, Özdenk G. Short-Term Effectiveness of Kinesio Taping in Patients With Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. 2017;26(6):470-478. doi:10.1123/jsr.2016-0132
- van der Sande R, Rinkel WD, Gebremariam L, Hay EM, Koes BW, Huisstede BM. Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: Effectiveness of Physiotherapy and Manual Therapy. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2014;48(16):1202-1208. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2013-093130
- Yamamoto N, Yamanaka K, Yasui K, et al. Shoulder stiffness after rotator cuff repair: A prospective randomized clinical trial comparing four different modalities. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery. 2011;20(4):609-615. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2010.11.025